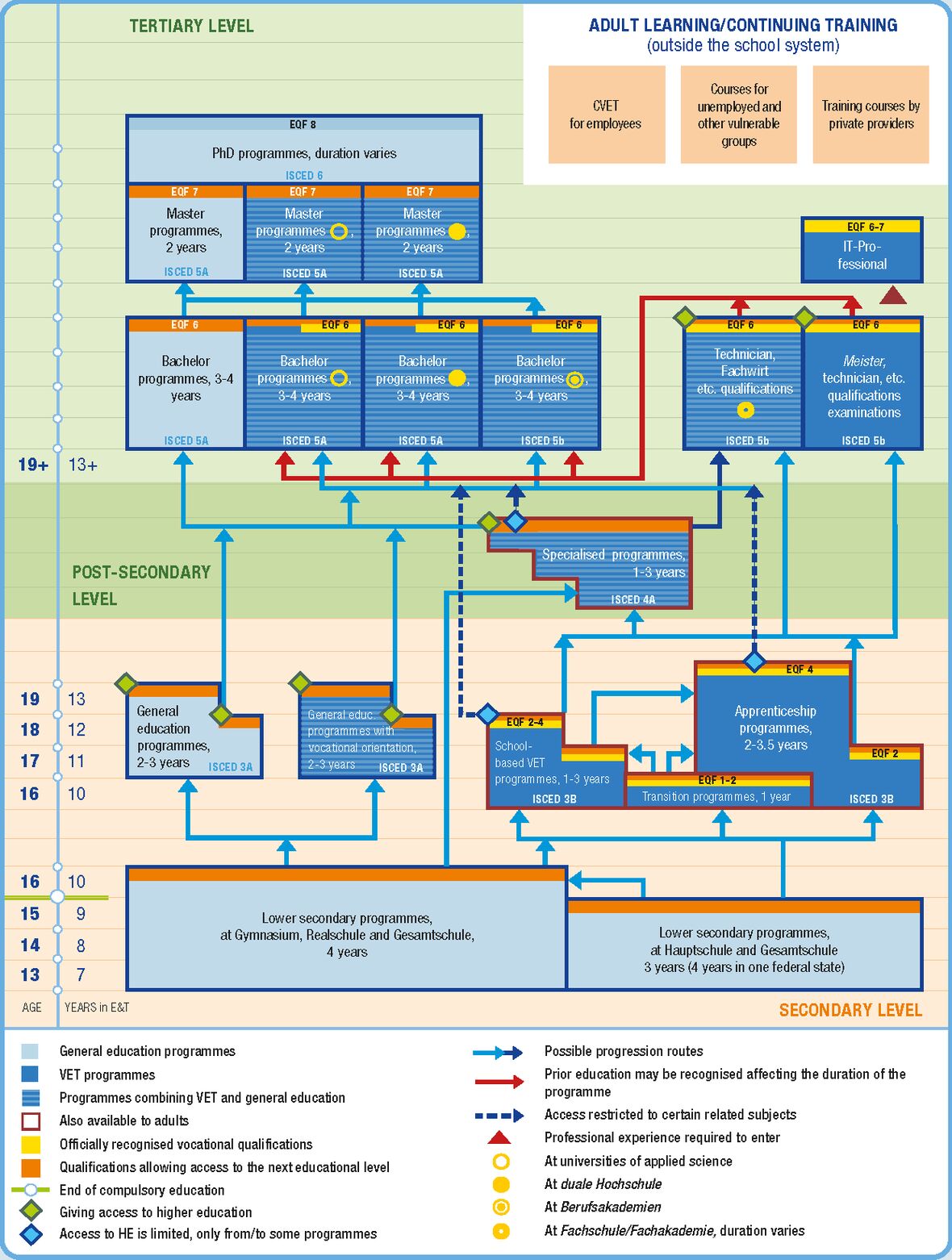
Education System and VET System
In Germany the Federal States are responsible for the field of education. In initial vocational education young people have the choice between apprenticeships and fulltime vocational schools. For graduates both systems offer pathways for professional advancement.
Compulsory education and certificates
Due to the cultural sovereignty the education systems of the Federal States differ slightly. Full time school attendance in Germany is compulsory for ten years starting at age 5 or 6, depending on the state. Pupils that are not continuing full time general or vocational school after those ten years are subject to the compulsory part time vocational school attendance until they turn 18 or for the duration of their apprenticeship in the dual system. After 4 or 6 years in primary education (depending on the federal state) pupils continue in different educational tracks (secondary general school, intermediate general school, grammar school or a comprehensive school combining the other types). Depending on the school type they can achieve five different leaving certificates:
- the general secondary education leaving certificate after Grade 9,
- the secondary education leaving certificate after Grade 10,
- the school part of the university of applied sciences entrance qualification (Fachhochschulreife) after Grade 11,
- subject-restricted university entrance qualification (Fachgebundene Hochschulreife) and
- the university entrance qualification (Abitur) after Grade 12 respectively 13.
Initial VET
When choosing initial VET, graduates with the secondary education leaving certificate can enter full-time vocational schools leading to a state certified occupation, general education programmes with vocational orientation or dual apprenticeship programmes.
The dual apprenticeship system dominates in terms of number of learners the German VET system and leads to recognized training occupations. Apprenticeship is open to anyone having finished compulsory education and having a contract with a training company. Pre-vocational training measures are available for young people that did not succeed in finding a training company to start an apprenticeship or are in need of upgrading their knowledge and competences.
The full-time vocational school system encompasses the VET programmes outside the dual apprenticeship system, which are regulated by other federal or federal state laws. Those are for example occupations in the health and the social sector or the so-called assistant occupations. Many occupations in the health sector also encompass two learning venues, e.g. a hospital and the vocational school.
Another option is programmes that combine general upper secondary and vocationally oriented education, usually leading to a university entrance qualification.
Formal continuing vocational education and training (CVET)
CVET in Germany is characterised by a broad range of offers and functions as an open market. For VET graduates nationally regulated further training qualifications are available, e.g. the “Meister (master craftsperson)” (EQF 6) and qualifications issued by the chambers. Both are based on the Vocational Training Act and the Trade and Crafts Code. The qualifications are mostly mapped on EQF-levels 5-7.
The trade and technical schools of the Federal States also offer state recognized VET qualifications at a higher level, e.g. to become a technician (EQF 6). Most further training qualifications and certificates of trade and technical schools enable access to university.
Tertiary system
German universities and universities of applied sciences offer bachelor and master programmes. The dual university, vocational academies and universities of applied sciences also run dual study programmes that combine learning at the higher education institution and the company.
German Qualifications Framework
The German Qualifications Framework for Lifelong Learning (GQF) was developed involving the relevant stakeholders and adopted in 2013. The GQF has eight levels to which formal qualifications from general education, higher education and vocational education are assigned. The concept of action competence is at the centre of the GQF. In the vocational sphere it is equated with vocational capacity as defined in the Vocational Training Act.
The two-year occupations of the dual system are assigned to level 3, the three-year and three-and-a-half-year occupations to level 4. Advanced training occupations in the CVET sector are assigned up to level 7. In 2017 also the general education diplomas were assigned, placing the university entrance qualification at level 4 in line with most dual VET occupations.